Mi In Ecg

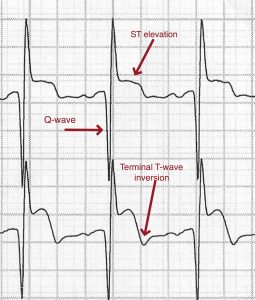
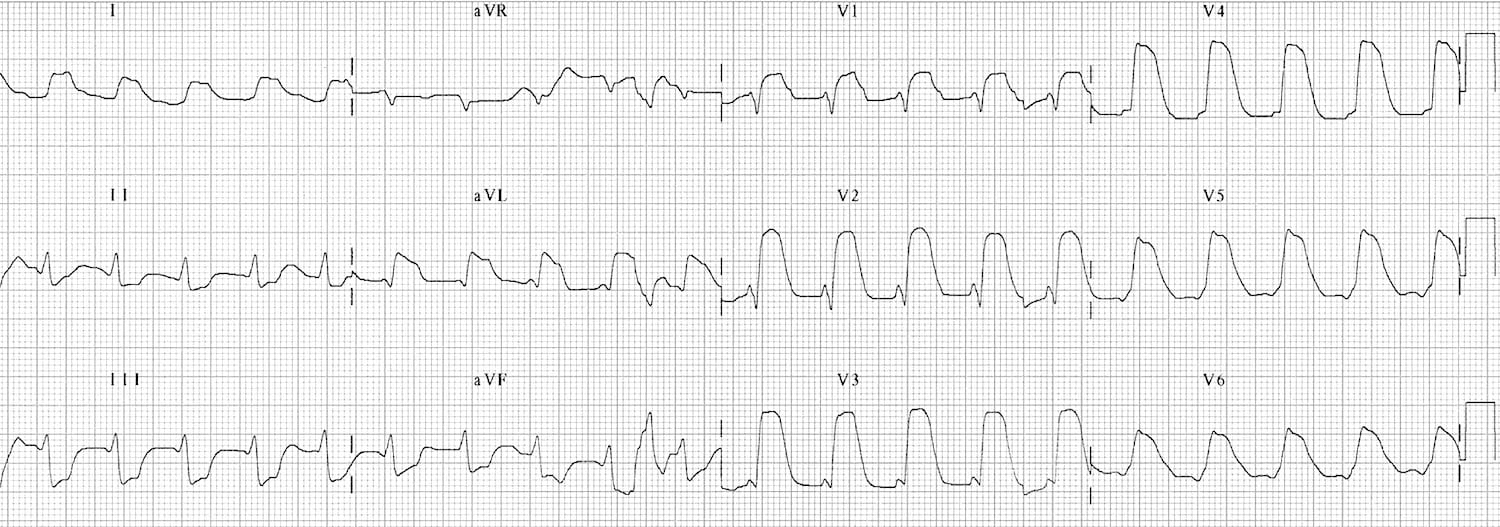
Mi s resulting from total coronary occlusion result in more homogeneous tissue damage and are usually reflected by a q wave mi pattern on the ecg.
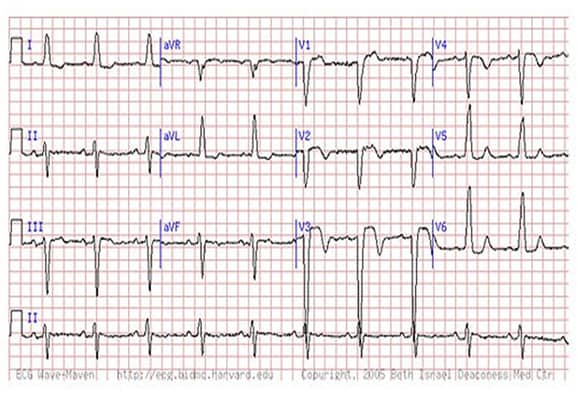
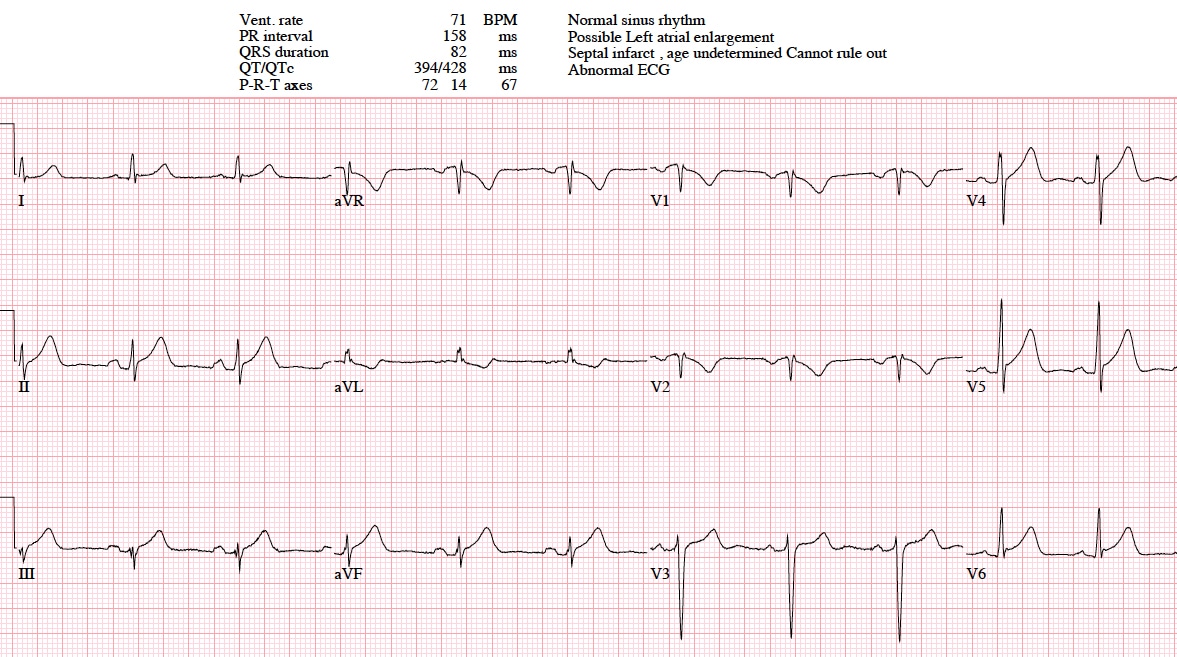
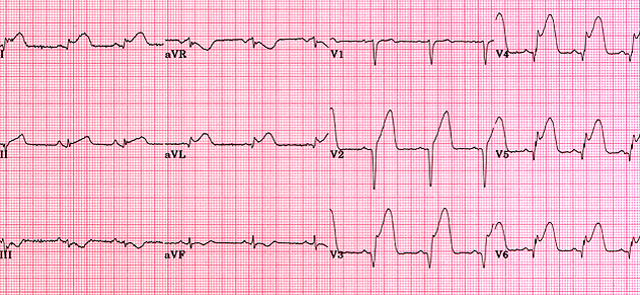
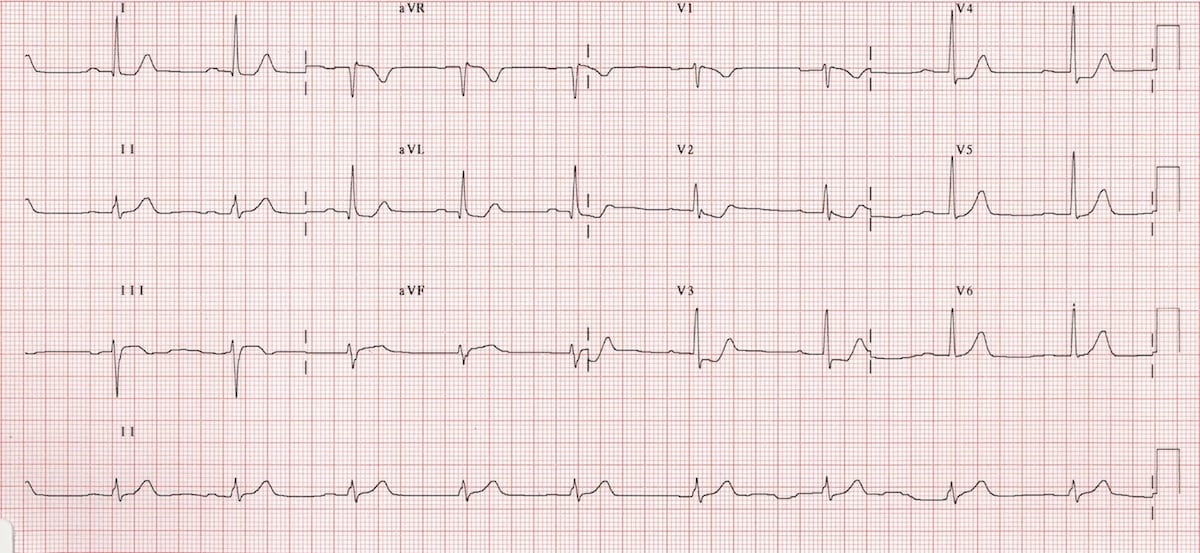
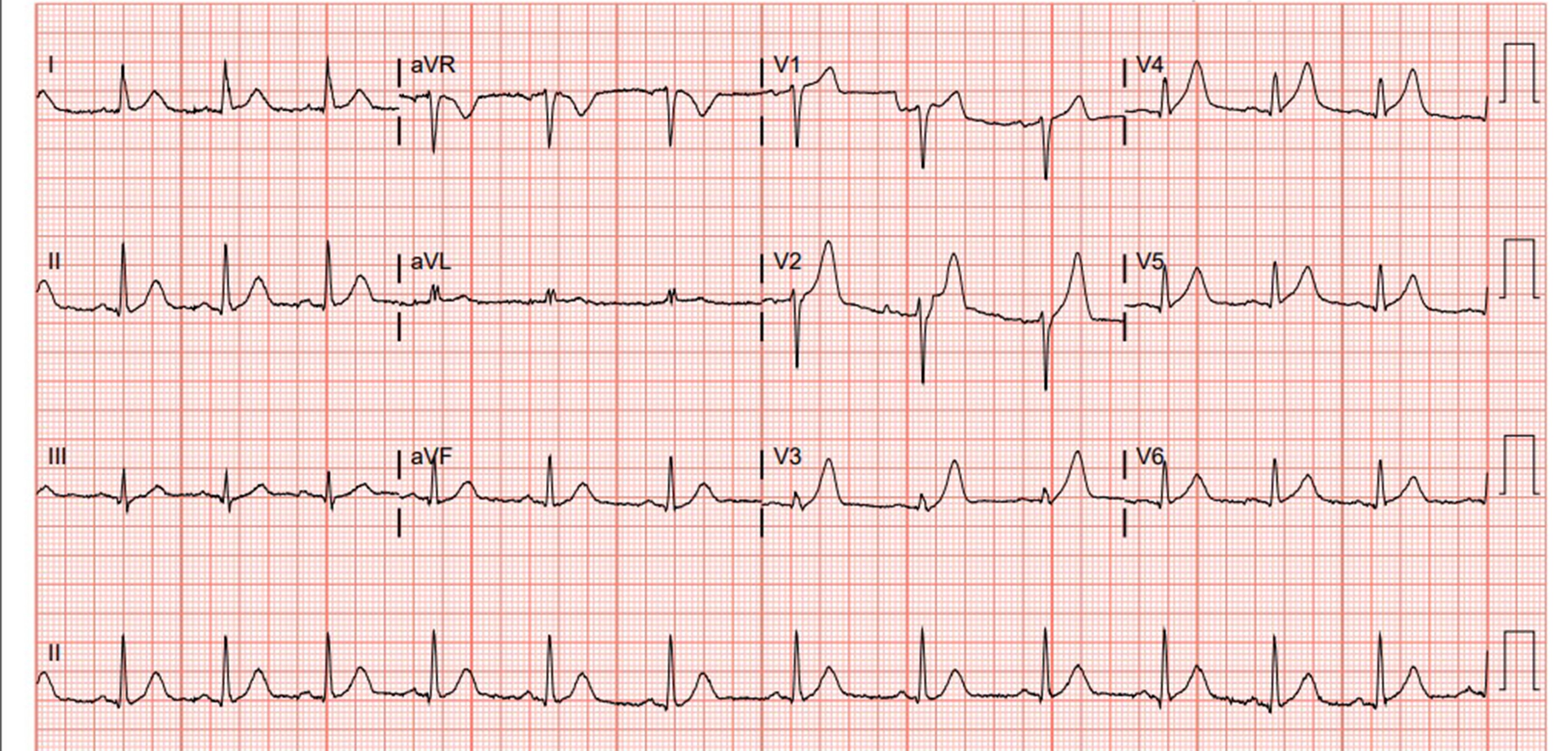
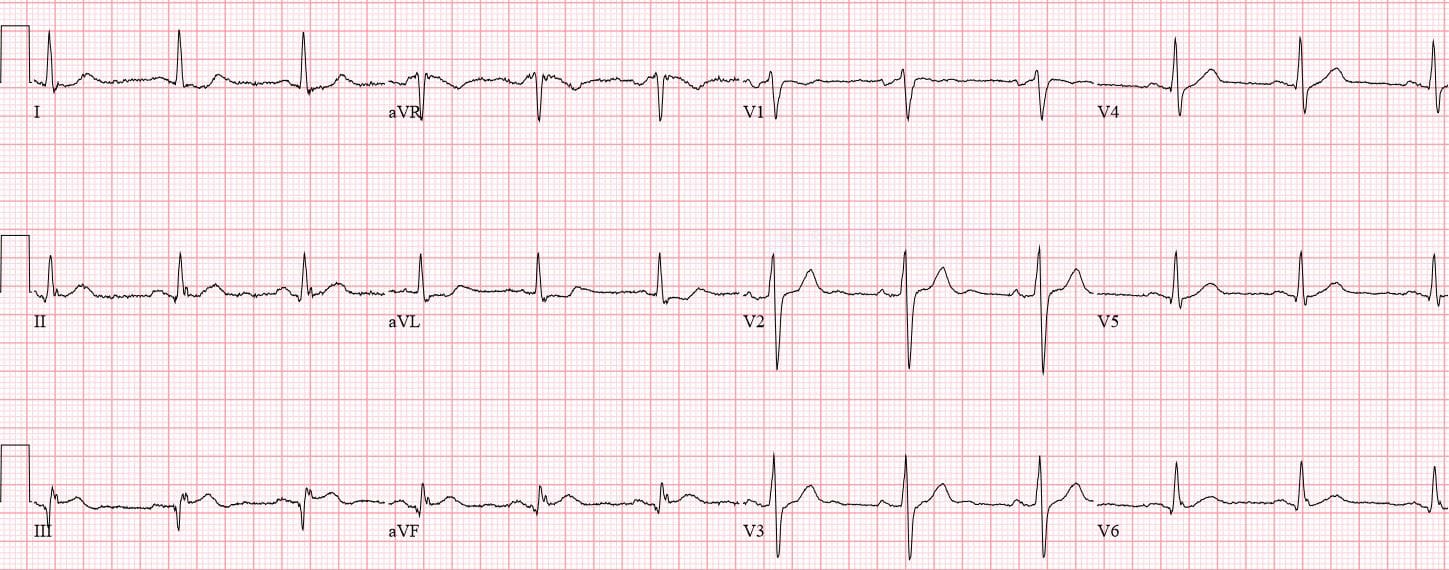
Mi in ecg. Elevated blood levels of cardiac enzymes ckmb or troponin t and. Pathological q waves develop on the ecg. A myocardial infarction is defined as. Old anterior wall myocardial infarction mi 12 lead ecg.
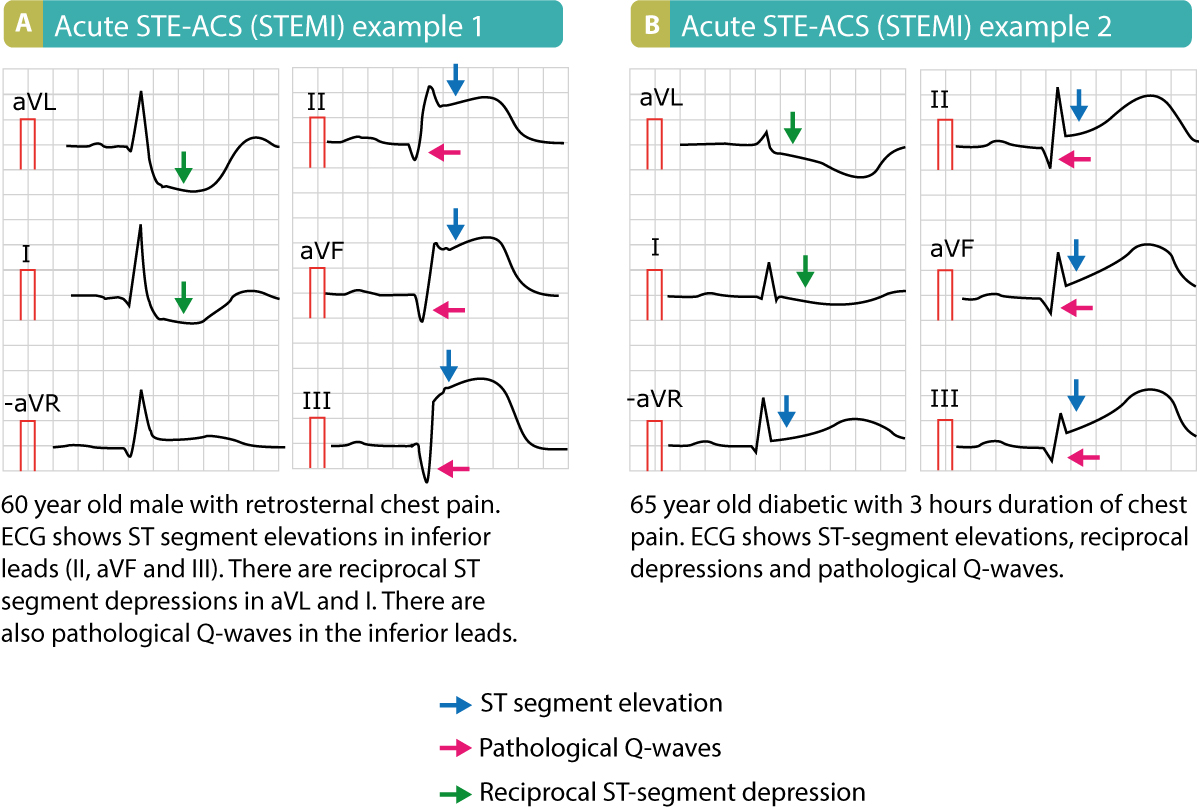
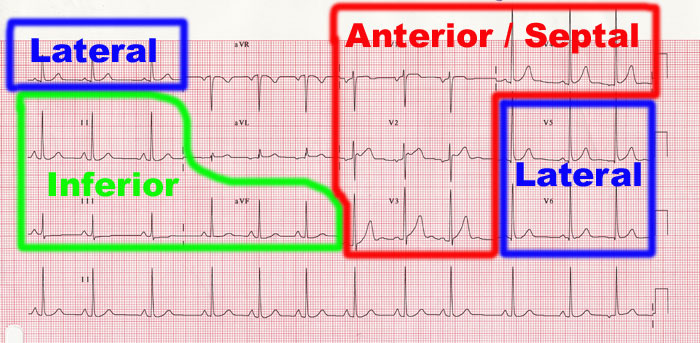
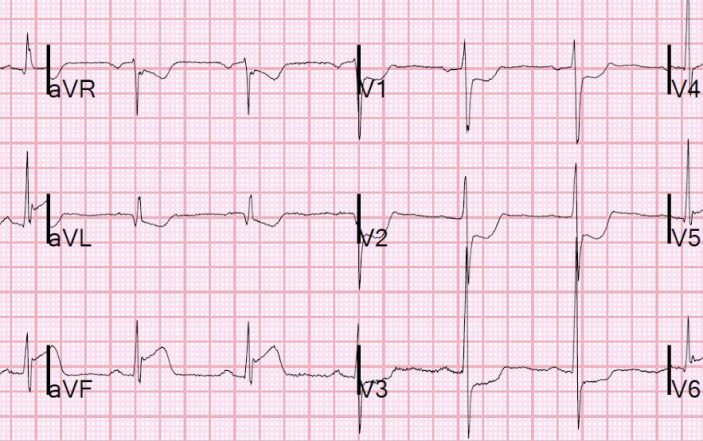
The patient has typical complaints the ecg shows st elevation or depression. Ecg library homepage clinical significance of posterior mi posterior infarction accompanies 15 20 of stemis usually occurring in the context of an inferior or lateral infarction. Electrocardiography in suspected myocardial infarction has the main purpose of detecting ischemia or acute coronary injury in emergency department populations coming for symptoms of myocardial infarction mi. A study comparing outcomes from anterior and inferior infarctions stemi nstemi found that on average patients with anterior mi had higher incidences of in hospital mortality 11 9 vs 2 8 total mortality 27 vs 11 heart failure 41 vs 15 and significant ventricular ectopic activity 70 vs 59 and a lower ejection fraction on admission 38 vs 55 compared to patients with inferior mi.
Missing a st segment. One of the complications with using ecg for myocardial infarction diagnosis is that it is sometimes difficult to determine which changes are new and which are old. Identifying an acute myocardial infarction on the 12 lead ecg is the most important thing you can learn in ecg interpretation. Time is muscle when treating heart attacks.
Also it can distinguish clinically different types of myocardial infarction. Isolated posterior mi is less common 3 11 of infarcts. 2015 acc aha scai focused update on primary pci for patients with stemi. The diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction is not only based on the ecg.
One of the following criteria are met.